No products in the cart.
Have you ever stopped to think about how your diet affects the planet? The food choices we make have a significant impact on the environment, and one of the most sustainable options is a vegetarian diet. But what are the environmental benefits of being vegetarian? In this blog, we’ll explore the environmental impact of a vegetarian lifestyle and why it might just be one of the most effective ways to make a positive difference in our world.
What is Vegetarianism?
Vegetarianism is a lifestyle that actively avoids the use or consumption of any animal product. For example, this includes meat, dairy, eggs, and other animal-derived ingredients. Furthermore, vegetarians also steer clear of non-food items like leather, wool, and cosmetics tested on animals.
Additionally, many people choose this way of life in an effort to lessen their environmental effect and support animal welfare. Vegetarians strive to live a more humane and ecological lifestyle by concentrating on plant-based options.
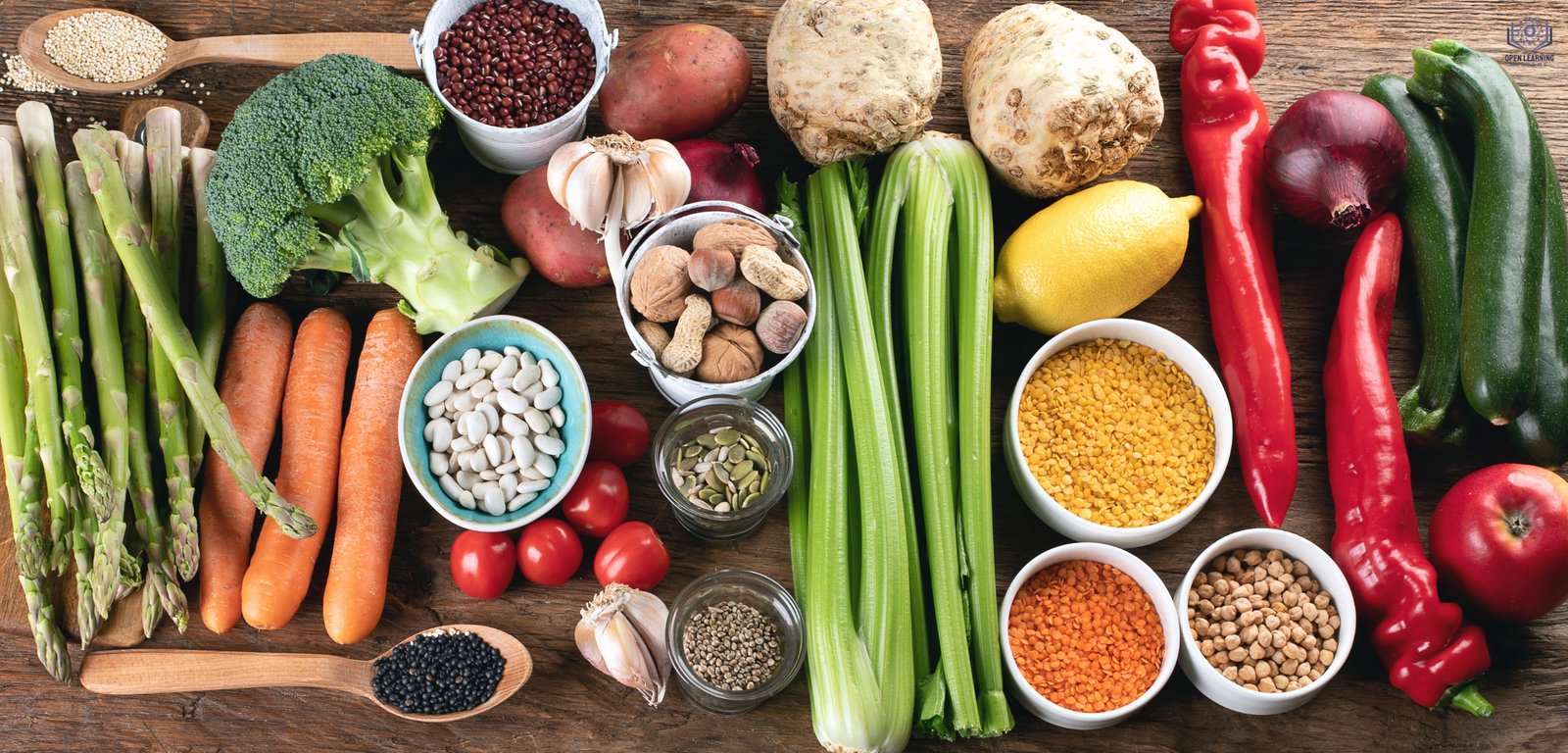

What Are the Environmental Benefits of Being a Vegetarian?
Below are some of the environmental benefits of being a vegetarian:
Reduce Carbon and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the easiest ways to reduce your carbon footprint is by switching to a vegetarian diet. The livestock industry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane and carbon dioxide. Methane, which is emitted during digestion by animals like cows, traps heat in the atmosphere at much higher rates than carbon dioxide.
Moreover, raising animals for meat requires energy-intensive processes such as breeding, feeding, and transporting livestock. These processes release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the air. In contrast, plant-based food production produces far fewer emissions. For example, growing vegetables or grains emit only a fraction of the gases produced by meat farming.
Requires Less Land
The environmental benefits of being vegetarian also include reducing the amount of land needed for food production. Raising livestock requires large areas of land for grazing and growing animal feed. To create this space, forests and natural habitats are often cleared, which leads to deforestation and a loss of biodiversity.
Plant-based diets are much less land-intensive. Crops grown for direct human consumption use far less space compared to those used to feed livestock. For example, growing grains, beans, and vegetables can support more people on the same plot of land than raising animals.
There is more room for forests, wildlife, and ecosystems to survive when humans require less land for food production. By doing this, the natural environment and biodiversity are safeguarded for coming generations.
Produces Fewer Emissions
Another important benefit of being vegetarian is the reduction of harmful emissions beyond carbon dioxide. Livestock farming generates huge amounts of waste, including manure, which produces ammonia and nitrous oxide. These gases contribute to air pollution and can harm both the environment and human health.
Additionally, animal farming relies on fertilisers and pesticides to grow animal feed, which then contaminates the soil and waterways. These chemicals lead to the growth of harmful algae and further pollute the water, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
Vegetarian diets, on the other hand, produce far fewer harmful emissions. Plant-based farming focuses on growing fruits, vegetables, and grains, which typically require f less chemical use and usually generate less waste. As a result, this dietary choice helps minimise pollution and creates cleaner air, soil, and water.
Conserves Water
Water scarcity is a growing concern worldwide, and the livestock industry is one of the largest consumers of water. Producing meat requires massive amounts of water for drinking, cleaning, and growing animal feed. For example, producing just one pound of beef can require over 1,800 gallons of water.
On the other hand, plant-based food production requires very little water. Fruits, vegetables, and grains are some of the crops that hardly require water to grow., which makes it a more sustainable choice. By shifting to a vegetarian diet, you can drastically reduce your water footprint.
Conserving water is especially important in areas where access to clean water is limited. A vegetarian lifestyle not only helps protect this vital resource but also ensures its availability for future generations.
Conserving water is especially important in areas where access to clean water is limited. A vegetarian lifestyle not only helps protect this vital resource but also ensures its availability for future generations.
Conclusion
The environmental benefits of vegetarianism are crystal clear: reducing greenhouse gas emissions, land use, toxic emissions, and conserving water, a vegetarian diet offers a sustainable way to protect the planet. Small changes in the way we eat can add up to make a big difference for the environment. Whether you choose to fully follow a vegetarian lifestyle or simply cut back on meat, every step you take to a healthier, more sustainable world is beneficial. So, why not give it a try? By making thoughtful dietary decisions, we can all play a part in creating a better future for our planet.
To help you get started, the Vegetarian Cookery Course from Open Learning Academy offers you the skills and knowledge to prepare delicious, environmentally-friendly meals that benefit both your health and the planet. Join today and take your first step towards a greener future!




